SMi Source lesson Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Prevention has the following microlearning topics
1. Why Assess Risk


2. What Works: Assessment and Intervention

Lesson Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Prevention teaches these concepts
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Why Assess Risk
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Why Assess Risk, Brief Interventions
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Preventing Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Interactive Exercise: Getting the Message Out
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Moderate Drinking/Social Drinking
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, The Benefits of Screening
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Alcohol-Exposed Pregnancies
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Prevention: Introduction, Reducing Alcohol-Exposed Pregnancies
Lesson Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Prevention addresses these key points
Why Assess Risk?
- To identify patients that may benefit from alcohol counseling
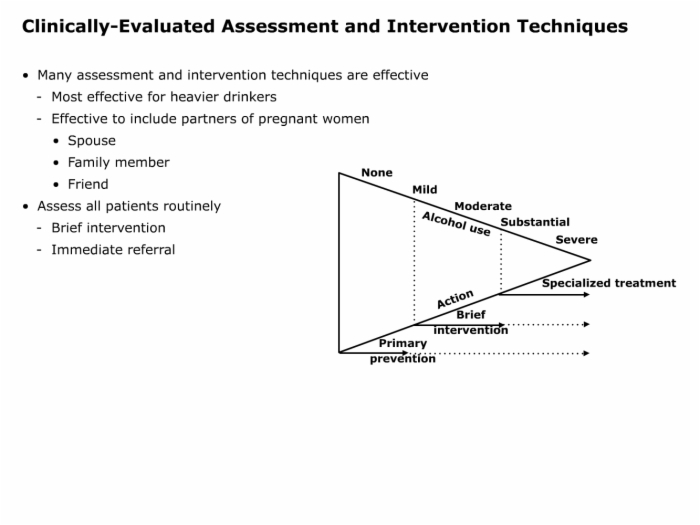
Brief Interventions
- Clinical research supports the effectiveness of screening and brief interventions to reduce alcohol consumption
Preventing Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
- Brief interventions help prevent alcohol-exposed pregnancies and promote healthy children
- FASD: An umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur in an individual whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy
What do you think? In the 2006 study by O'Connor and Whaley of low income women, what percentage of women who drank while pregnant were not advised by their healthcare providers to stop?
- Of the women who continued to drink while pregnant, 40% were not advised by their healthcare providers to stop
Moderate Drinking/Social Drinking
- Effects
- Smaller size
- Decreased IQ scores
- More minor physical anomalies
- Adverse behavioral outcomes
- More learning disabilities
Prenatal development is adversely affected by social or moderate maternal drinking.
The Benefits of Screening
- Identifies patients before or between pregnancies
- Protects subsequent pregnancies from alcohol exposure
- Identifies patients before dependence
- Educates patients
- Dangers of drinking if pregnant
Alcohol-Exposed Pregnancies
- Birth defects
- Prevalence
- 40,000 babies born per year with FASD (1 in 100)
- 0.2 to 1.5 cases FAS per 1, 000 live births in U.S.
- Cost
- Lifetime cost for one individual with FAS in 2002 was $2 million
- Annual cost of FAS (2004) $4.0 billion
Prevention
- Active screening
- Nursing assistant 2-3 minutes of time
- $1.50 per patient
- Registered nurse 3 minutes
- $5.00 per patient
- Primary care physician 5 minutes
- $10.00 per patient
- Nursing assistant 2-3 minutes of time
- Intervention
- Primary care physician 5 minutes
- $10.00 per patient
- Mental health counselor 12-20 minutes per patient
- $48.00 to $80.00
- Primary care physician 5 minutes
- Reimbursement
- Medicaid and private payers
- HCPCS Codes (e.g H0001; alcohol and/or drug assessment)
- Medicaid and private payers
Healthcare providers are key educators regarding appropriate alcohol use.
Lesson Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Prevention is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
Astley SJ. Comparison of the 4-Digit Diagnostic Code and the Hoyme Diagnostic Guidelines for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Pediatrics. 2006;118(4):1532-1545.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Website. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs): Tracking Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS). Last updated: August 24, 2009. Accessed on January 18, 2010.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Guidelines for Referral and Diagnosis (CDC)
Lutpon C, Burd L, Harwood R. Cost of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Am J Med Genet. 2004;127C:42-50.
Manwell LB, Fleming MF, Johnson K, Barry KL. Tobacco, alcohol, and drug use in a primary care sample: 90 day prevalence and associated factors. J Addict Dis. 1998;17(1):67-81.
May PA, Gossage JP, Kalberg WO, et al. Prevalence and Epidemiologic Characteristics of FASD From Various Research Methods with an Emphasis on Recent In-School Studies. Disabilities Research Reviews. 2009;15(3):176-192.
Olson ,et al. National Task Force on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Effect. A call to action: Advancing Essential Services and Research on Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders – A report of the National Task Force on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Effect, March 2009. [Cost data: Lupton, et al., 2004]
The FASD Center, Dept. of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)