SMi Source lesson HCV: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Monitoring has the following microlearning topics
1. HCV Assays and Their Applications


2. HCV RNA Assay Technologies

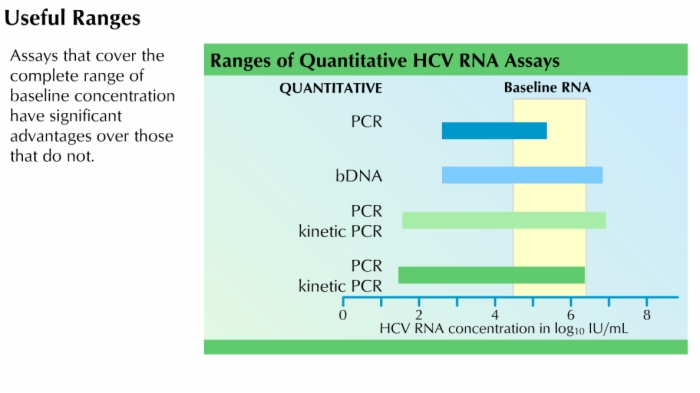
3. Useful Ranges

4. Guidelines for Therapeutic Monitoring


Lesson HCV: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Monitoring teaches these concepts
HCV Assays and Their Applications, Testing for HCV
HCV Assays and Their Applications, Molecular Components Detected by the Assays
HCV Assays and Their Applications, Antibody Assays
HCV Assays and Their Applications, HCV RNA Assays
HCV Assays and Their Applications, Test Yourself
HCV Assays and Their Applications, Core Antigen Assay
Lesson HCV: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Monitoring addresses these key points
A number of molecular asssays are available for the detection and monitoring of hepatitis C virus.
HCV assays can be classified according to:
- The substances they detect:
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids
- The technologies they employ
Appropriate type of assay depends on status of person to be tested, e.g.:
- Blood donors
- Those with high risk factors for HCV infection (screening)
- Those with signs or symptoms of hepatitis
- Those undergoing therapy for HCV
Molecular components:
- Glycoproteins
- Envelope
- Core protein
- Viral RNA
Anti-HCV antibody:
- Blood screening
- Diagnostic setting
Core protein:
- Core antigen assay
A number of HCV assays target the RNA of the viral genome — particularly sequences at the 5-prime end of the genome.
Anti-HCV antibodies can be detected in the blood.
EIA:
- HCV antigens
- Anti-HCV antibody
- Second antibody conjugate
Anti-HCV antibody tests are good indicators of past infection.
Antibodies do not appear until 7-8 weeks after infection.
Antibodies persist in patients with chronic hepatitis C, and even in some after infection has resolved.
In rare cases (e.g., immunosuppression or long-term hemodialysis), an HCV-infected patient will not express anti-HCV antibody.
Asssays target sequences within 5-prime noncoding (5' NC) region of the HCV genome.
HCV RNA assays do not involve antibodies.
HCV RNA assay classifications:
- Qualitative assays:
- Optimized to detect the smallest quantity of HCV RNA possible
- Specific for HCV
- Answer the question: present of absent?
- Negative result: indicates that virus cannot be detected, and in the context of therapy, suggests resolution of the infection
- Quantitative assays:
- Designed to determine the concentration of virus in a person's blood (quantify the viral load)
- Answer the question: how much?
- Establish a baseline viral load after diagnosis
- Track the changes in viral load during therapy
- Less sensitive than qualitative assays; optimized for a number of performance characteristics besides sensitivity
- Amount of virus reported in international units (IU); concentration: IU/mL
- Genotyping assays:
- Determine the genotype of the virus affecting a particular patient
- Differentiate between RNA sequences that mark the different genotypes
- Genotype designations: 1, 2, 3, etc.
- Subtype designations: 1a, 1b, 2a, etc.
Qualitative assays:
- Optimized to detect the smallest quantity of HCV RNA possible
Quantitative assays:
- Designed to determine the concentration of virus in a person's blood (quantify the viral load)
Genotyping assays:
- Differentiate between RNA sequences
Core antigen assay:
- Immunoassay
- Core antigen present in a sample binds to anti-core antibody attached to the surface of a microtiter well
- A second antibody conjugate is applied next
- A reaction catalyzed by the enzyme part of the antibody conjugate causes a color change and reports the presence of the core antigen
- Performance characteristics not nearly as well established as for RNA-based assays
- Less sensitive than the quantitative HCV RNA assays
Lesson HCV: Diagnosis and Therapeutic Monitoring introduces and defines these terms
EIA = Enzyme Immunoassays