SMi Source lesson Insomnia: GABA Mechanism of Action has the following microlearning topics
1. Treatment of Insomnia

Lesson Insomnia: GABA Mechanism of Action teaches these concepts
GABA Mechanism of Action, Mechanism of Action: Introduction
GABA Mechanism of Action, Mechanism of Action, Benzodiazepines
GABA Mechanism of Action, Mechanism of Action, Non-Benzodiazepines
Lesson Insomnia: GABA Mechanism of Action addresses these key points
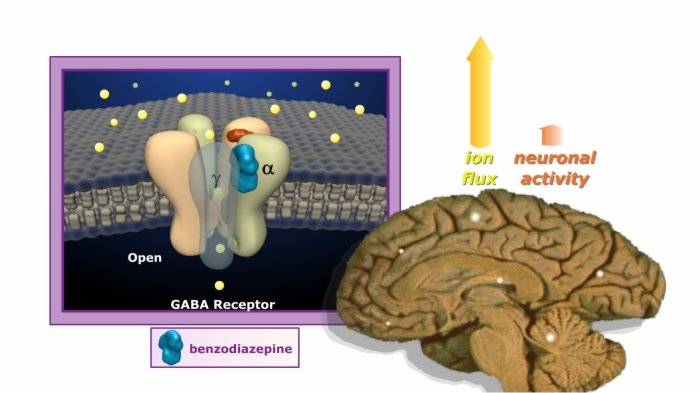
Many prescription sleep aids potentiate GABA
- Inhibitory neurotransmitter
- Binds to the GABA-A receptor, which is composed of several different subunits
- GABA-A receptor opens an ion channel through which chloride ions enter the cell and inhibit neuronal activity
Benzodiazepines
- Believed to treat insomnia because of their ability to bind to an allosteric site on the GABA-A receptor
- Site is a pocket-situated between two subunits: alpha and gamma
- They do not discriminate which type of alpha-subunit they bind to
- Results in indiscriminate GABA-A receptor activation
Non-Benzodiazepines
- Bind more selectively to GABA-A receptors containing the alpha-1 subunit
- Lower selectivity for the subunits other than alpha-1
- Anxiolytic muscle relaxant and amnestic effects