SMi Source lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome has the following microlearning topics
1. Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes

2. Presentation and Diagnosis

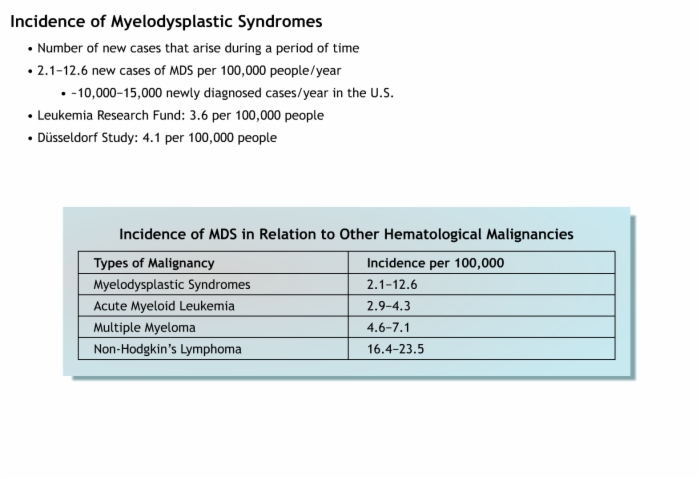
3. Epidemiology and Incidence

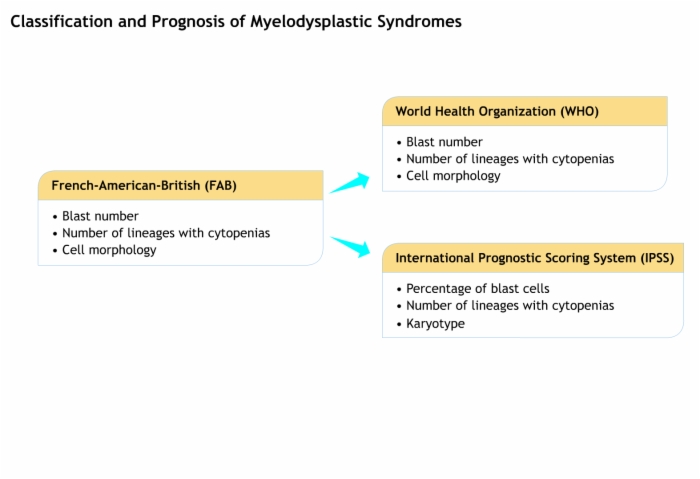
4. Classification and Prognosis

5. Summary: Myelodysplastic Syndromes

Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome teaches these concepts
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Normal Hematopoiesis
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Normal Hematopoiesis: Pluripotent and Multipotent Stem Cells
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Normal Hematopoiesis: Amplification of Committed Progenitor Cells
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Normal Hematopoiesis: Factors that Influence Hematopoietic Cell Proliferation, Differentiation and Survival
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Abnormal Hematopoiesis: Cytopenia
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Abnormal Hematopoiesis: Later MDS and Abnormal Blood Cell Morphology
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Abnormal Hematopoiesis: Early MDS
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Abnormal Hematopoiesis: Abnormal Cytogenetics
Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Introduction to Myelodysplastic Syndromes, Interactive Exercise: Cancer Vocabulary
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome addresses these key points
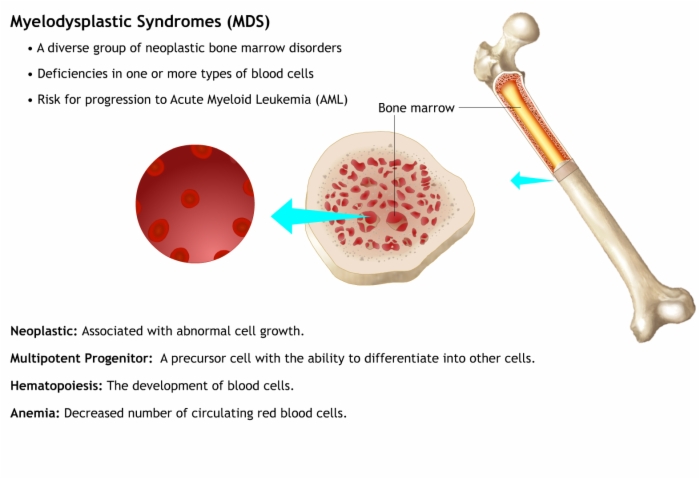
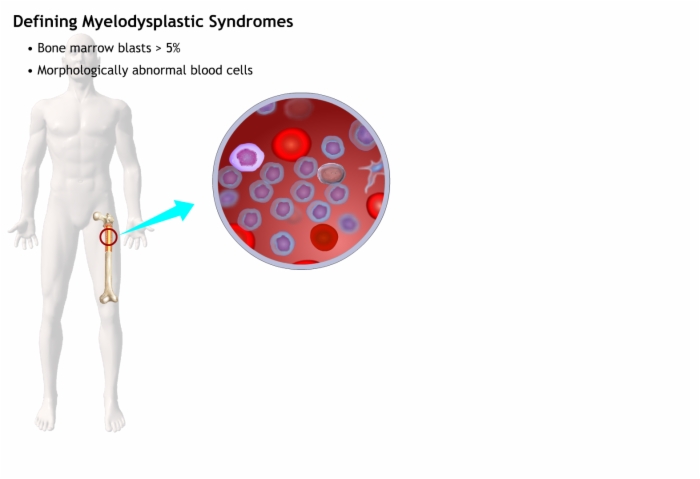
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
- A diverse group of neoplastic bone marrow disorders
- Deficiencies in one or more types of blood cells
- Risk for progression to Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Normal Hematopoiesis
- Types of Blood Cells
- Red blood cells: Erythrocytes
- Oxygen Transport
- White blood cells: Leukocytes
- Fight Infection
- Platelets: Thrombocytes
- Blood Coagulation
- Red blood cells: Erythrocytes
Pluripotent and Multipotent Stem Cells
- Pluripotent: Able to generate numerous cell types.
- Multipotent: Able to generate a limited number of cell types.
Normal Hematopoiesis
- Amplification of Committed Progenitor Cells
Terminally differentiated: Specialized cells that are unable to proliferate.
Normal Hematopoiesis
Factors that Influence Hematopoietic Cell Proliferation, Differentiation and Survival
- Growth Factor: Stem Cell Factor (SCF)
- Colony Stimulating Factor(CSF): Erythropoietin (EPO)
Abnormal Hematopoiesis
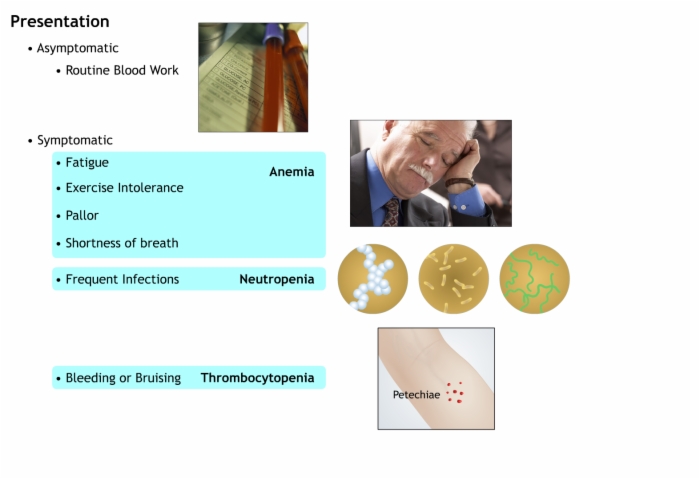
- Cytopenia: Decreased mature, circulating blood cells
- Red Blood Cells: Anemia
- White Blood Cells: Neutropenia
- Platelets: Thrombocytopenia
Abnormal Hematopoiesis- Later MDS
- Increased Proliferation
- Loss of Differentiation
- Decreased Apoptosis
Abnormal Blood Cell Morphology
- Normal Erythroblast
- Ringed Sideroblast
- Auer Rods
- Morphology: The form and structure of a cell
Increased Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death):
- Occurs as a normal part of the development of an organism and its tissues
- Caused by changes in the bone marrow microenvironment that lead to an overproduction of factors such as tumor necrosis factor alpha
Abnormal Cytogenetics - Trigger for Abnormal Hematopoiesis
- Epigenetic: Heritable changes in DNA that do not result in changes in DNA sequence
- Cytogenetic: Heritable changes in chromosomes or genes within chromosomes
Myelodysplastic syndromes are a heterogeneous group of acquired bone marrow disorders of altered hematopoiesis resulting in peripheral cytopenias.
Hematopoiesis: The formation and development of blood cells in the bone marrow
Cytopenias: A reduction in the number of cells in the blood
Transformation: The change that a normal cell undergoes as it becomes malignant
Acute Leukemia: A rapidly progressing cancer of the blood-forming tissue in the bone marrow
Dysplasia: Abnormal cell growth
Morphology: The form or structure of a cell or organ
Apoptosis: Programmed cell death
Proliferation: An increase in the number of cells as a result of cell growth and cell division
Epigenetic: Heritable changes in DNA that do not result in changes in DNA sequence
Cytogenetic: Heritable changes in chromosomes or genes within chromosomes
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
D.P. Steensma and J.M. Bennett. The Myelodyplastic Syndromes: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006.
B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, P. Walter. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th Edition. Garland Science of the Taylor & Francis Group. New York, N.Y., 2002.
D.V.T. Catenacci and G.J. Schilller. Meyelodyplastic Syndromes: A Comprehensive Review. Blood Reviews. 2005.
H.T. Nishino, C.-C. Chang. Myeolodysplastic Syndromes. Clinicopathologic Features, Pathobiology, and Molecular Pathogenesis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2005.
G. Yue, S. Hao, O. Fadare, S. Baker, O. Pozdnyakova, N. Galili, B.A. Woda, A. Raza, S.A. Wang. Hypocellularity in Myelodysplastic Syndrome is an Independent Factor Which Predicts a Favorable Outcome. Leukemia Research. 2008.
D. Marisavljevic, V. Cemerikic, Z. Rolovic, D. Boskovic, M. Colovic. Hypocellular Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Clinical and Biological Significance. Medical Oncology. 2005.
P.L. Greenberg, N.S. Young and N. Gatterman. Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2002.
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome introduces and defines these terms
Neoplastic: Associated with abnormal cell growth.
Hematopoiesis: The development of blood cells.
Multipotent Progenitor: A precursor cell with the ability to differentiate into other cells.
Anemia: Decreased number of circulating red blood cells.
AML = Acute Myeloid Leukemia
MDS = Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Red blood cells: Erythrocytes
White blood cells: Leukocytes
Platelets: Thrombocytes
Pluripotent: Able to generate numerous cell types.
Multipotent: Able to generate a limited number of cell types.
Terminally differentiated: Specialized cells that are unable to proliferate.
SCF = Stem Cell Factor
CSF = Colony Stimulating Factor
EPO = Erythropoietin
Anemia: Decreased number of ciruclating red blood cells.
Neutropenia: Decreased number of circulating neutrophils (white blood cells).
Thrombocytopenia: Decreased number of circulating platelets.
Morphology: The form and structure of a cell
TNFα = Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
Epigenetic: Heritable changes in DNA that do not result in changes in DNA sequence
Cytogenetic: Heritable changes in chromosomes or genes within chromosomes.