SMi Source lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Changes in Apoptosis has the following microlearning topics
1. Changes in Apoptosis

2. Cytopenias in MDS

3. Mutations in Genes Responsible for Cell Proliferation

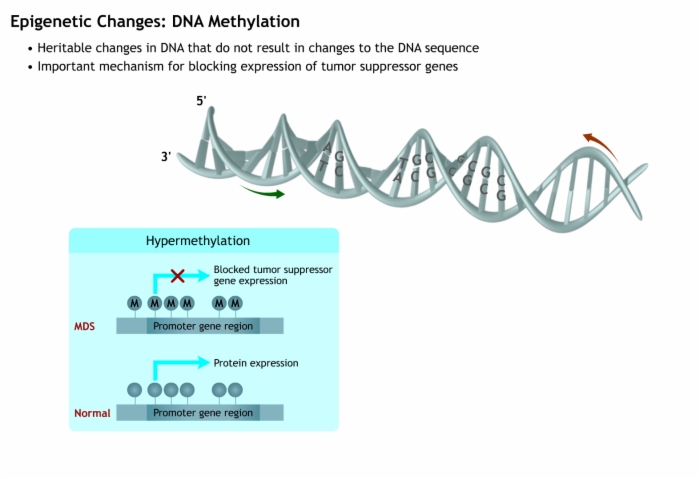
4. Gene Silencing: DNA Methylation

5. Chromosome Abnormalities in MDS
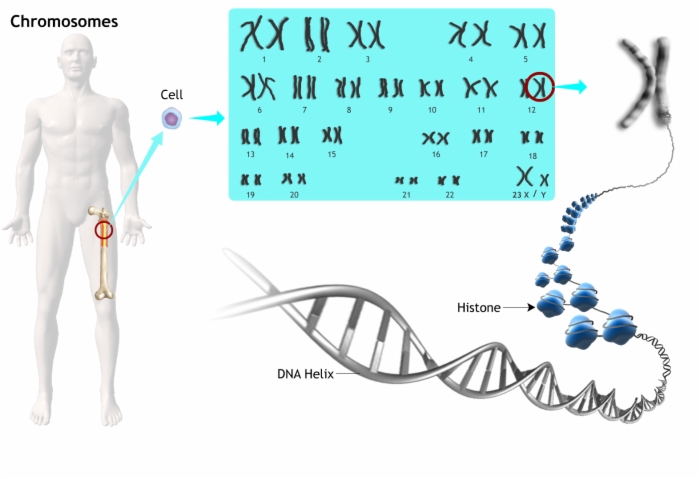

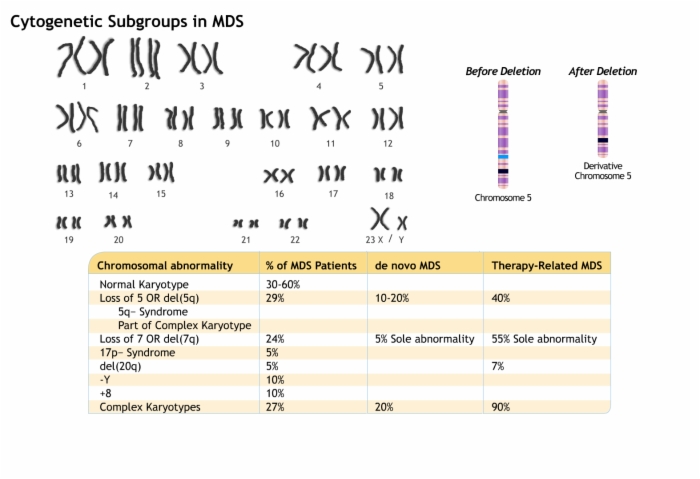
6. Cytogenetic Subgroups in MDS

Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Changes in Apoptosis teaches these concepts
Cytopenias and Gene Mutations in MDS, Changes in Apoptosis
Cytopenias and Gene Mutations in MDS, Deficiencies in Circulating Blood Cells
Cytopenias and Gene Mutations in MDS, Decreases in Apoptosis as MDS Progresses
Cytopenias and Gene Mutations in MDS, Increases in Apoptotic Cytokine Production
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Changes in Apoptosis addresses these key points
Apoptotic cell signal
- Apoptosis: Programmed cell death.
- Proliferation: Cell growth, division and propagation.
- Hematopoietic: Having to do with the development and production of blood cells.
- Cytopenias: Deficiency of peripheral blood cells.
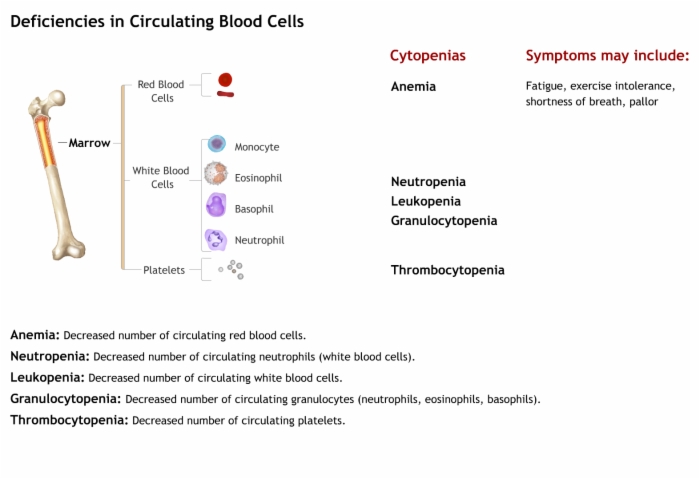
Deficiencies in Circulating Blood Cells
Cytopenias:
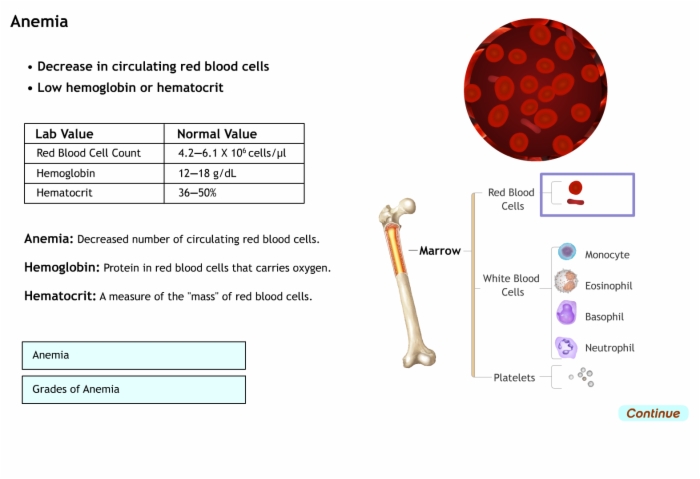
- Anemia: Decreased number of circulating red blood cells.
- Neutropenia: Decreased number of circulating neutrophils (white blood cells)
- Leukopenia: Decreased number of circulating white blood cells.
- Granulocytopenia: Decreased number of circulating granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
- Thrombocytopenia: Decreased number of circulating platelets.
Symptoms include:
- Anemia: Fatigue, exercise intolerance, shortness of breath, pallor
- Neutropenia: Frequent infections and fever
- Thrombocytopenia: Bruising and bleeding
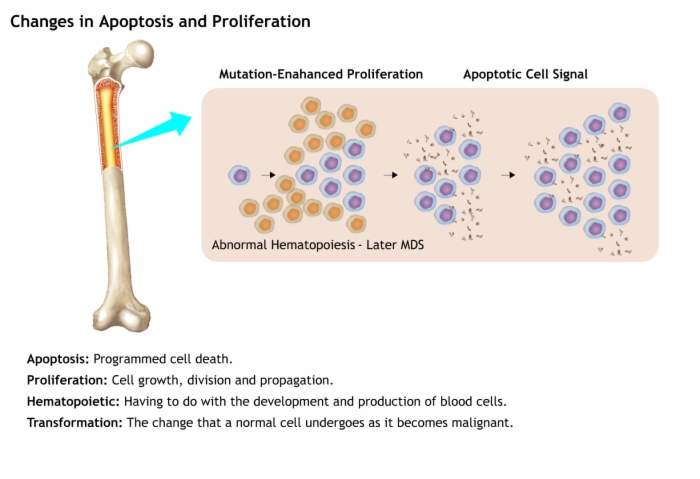
Early in MDS, there are increases in apoptosis, whereas later as MDS progresses, there may be decreases in apoptosis.
- These contribute to the development and progression of MDS.
- Increased hematopoietic cell apoptosis, results in cytopenias.
Increases in Apoptotic Cytokine Production
- Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNFα)
- Ligand for the Fas receptor
- Interferon gamma (INFγ)
As MDS progresses, there is increased proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells as well as decreased apoptosis of those precursor cells, resulting in an increased number of dysfunctional cells.
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Changes in Apoptosis is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
D.P. Steensma and J.M. Bennet. The Myelodysplasic Syndromes: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006.
D.V.T. Catenacci and G.J. Schiller. Myelodysplastic Syndromes. A Comprehensive Review. Blood Reviews. 2005.
D.T. Bowen, E. Hellström-Lindberg. Treatment of Anemia in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. From the Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Pathobiology and Clinical Management. Edited by J.M. Bennett. Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York, N.Y. 2002.
https://www.blueshieldca.com/hw/articles/hw_article.jsp?articleId=HWHW4260&fromTopics=all_topics&_requestid=835042
http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=15737
H.T. Nishino and C.-C. Chang. Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Clinicopathologic Features, Pathobiology, and Molecular Pathogenesis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2005.
Lesson Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Changes in Apoptosis introduces and defines these terms
Apoptosis: Programmed cell death.
Proliferation: Cell growth, division and propagation.
Hematopoietic: Having to do with the development and production of blood cells.
Cytopenias: Deficiency of peripheral blood cells.
Anemia: Decreased number of circulating red blood cells.
Neutropenia: Decreased number of circulating neutrophils (white blood cells)
Leukopenia: Decreased number of circulating white blood cells.
Granulocytopenia: Decreased number of circulating granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
Thrombocytopenia: Decreased number of circulating platelets.
TNFα = Tumor Necrosis Factor
INFγ = Interferon gamma