SMi Source lesson Obesity: Drug Effects has the following microlearning topics
1. Normal ARC Function

Lesson Obesity: Drug Effects teaches these concepts
Obesity, Homeostatic Mechanisms, Normal ARC Function, Control of Energy Homeostasis
Obesity, Homeostatic Mechanisms, Normal ARC Function, The Weight Control Circuit
Obesity, Homeostatic Mechanisms, Normal ARC Function, Monoamines
Obesity, Homeostatic Mechanisms, Normal ARC Function
Lesson Obesity: Drug Effects addresses these key points
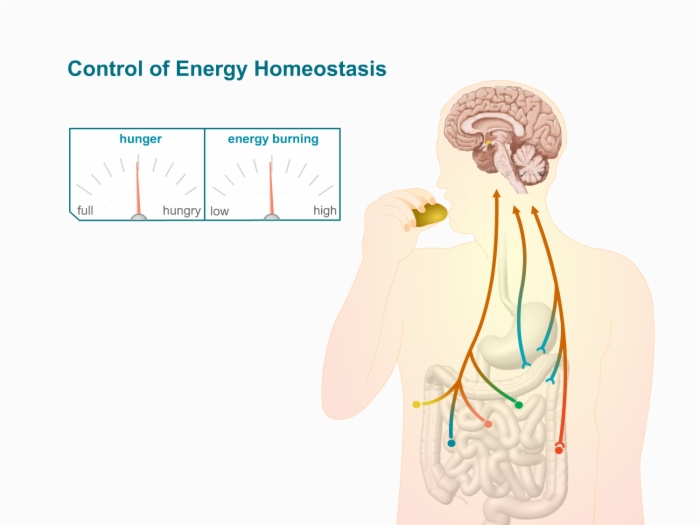
Control of energy homeostasis:
- Multiple pathways converge in brain to balance energy in with energy out
Arcuate nucleus:
- Region of convergence
- Neural network in the hypothalamus region
- Integrates hormonal and neural signals to balance food intake with energy expenditure to maintain a stable body weight
POMC neurons:
- Activated by anorexigenic or appetite suppressing signals
- Release α-MSH
- Activate MC4 receptor
- Reduce hunger/increase energy expenditure
- Release beta-endorphin
- Negative feedback to stop release of α-MSH
AgRP/NPY neurons:
- Activated by orexigenic or appetite stimulating signals
- Inhibited by appetite suppressing signals
- Release neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related protein (AgRP)
- Increase hunger/decrease energy expenditure
Monoamines:
- Stimulate neurons to send signals that increase energy expenditure and decrease hunger
Obesity:
- May occur when circuits of arcuate nucleus are ineffective
- Resistance to the leptin satiety signal
- May be treated with therapeutic agents that bypass signal resistance or substances useful in treating addictive disorders
Lesson Obesity: Drug Effects introduces and defines these terms
α-MSH = Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone
NPY/AgRP = Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-Related
POMC = Pro-Opiomelanocortin