SMi Source lesson Oncology Treatment: VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis has the following microlearning topics
1. Sorafenib Signal Transduction

Lesson Oncology Treatment: VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis teaches these concepts
Sorafenib Signal Transduction, VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, VEGF Production in Angiogenesis
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Activation of Ras
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Ras Activation of Raf/MEK/ERK
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Activating Mutations of Raf and Ras
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Signaling
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Ras/PI3 Kinase Signaling
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Akt Signaling and Proliferation
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Signaling
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Cyclin Dependent Kinase Regulation of Cell Cycle Genes
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, Akt Signaling and Cell Survival
VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis, Sorafenib Signal Transduction, PI3 Kinase, Rac1 and Cell Migration
Lesson Oncology Treatment: VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis addresses these key points
The VEGF family consists of:
- Glycoprotein homodimers that exhibit specific binding to VEGF receptors 1, 2 and/or 3
VEGF receptor 2 is considered to be the major mediator of VEGF-A angiogenic effects including:
- Cell proliferation
- Survival
- Migration
Soluble VEGF receptor 1
- Lacks transmembrane and intracellular regions
- Prevents VEGF-A binding to VEGF receptor 2
Hypoxia leads to:
- A sequence of molecular signals that results in the increased expression of VEGFA
- Binds to VEGF2 receptors on vascular endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis
Expression of VEGF is regulated by HIF-1
- Hydroxylated by a family of oxygen-dependent prolyl hydroxylases
- Expression leads to increased production of VEGF which results in vascular endothelial cell survival
- Increases PDGF expression which leads to increased survival of other vascular cells
Phosphorylated tyrosine kinase receptor
- Interacts with the Src homology 2 domain or SH2 domain of the adapter proteins Shc and Grb2
- Grb2 through its SH3 domains recruits Sos to the plasma membrane
- Sos activates the small G protein Ras by promoting the release of GDP in exchange for GTP
- GTP bound Ras activates and interacts with a variety of effectors including Raf/MAP Kinase, PI3 Kinase and Ral-GEF
Ras
- Recruits Raf to the cell membrane
Activated Raf
- Phosphorylates MAPK Kinase or MEK which in turn phosphorylates ERK 1 and ERK2
ERK
- Phosphorylates and activates a variety of transcription factors
Sorafenib
- Blocks the activation of the serine/threonine kinase Raf in addition to multiple receptor tyrosine kinases
When activating mutations of Ras or Raf occur, these signaling molecules become capable of eliciting downstream mitogenic responses independent of receptor stimulation.
Sorafenib
- Blocks Ras and Raf signaling by directly inhibiting Raf kinase activity
- MAP Kinases or ERK 1 and 2 phosphorylate a variety of transcription factors
- ETS transcription factors have a highly conserved DNA binding domain
- Ternary complex factors binds to a low affinity ETS binding domain with serum response factor or SRF on a serum response element in the promoter regions of many immediate early genes
- The AP-1 transcription factors are made up of homo- and hetero-dimers of c-fos and c-jun
- ERK regulation of transcription effects the levels of gene products that control the cell cycle
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Signaling
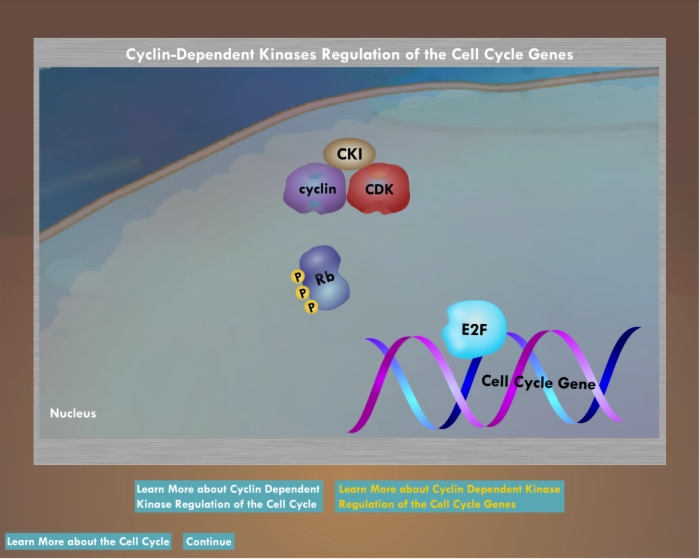
Cyclin Dependent Kinase Regulation of the Cell Cycle
- Enzymes that lead the cell through the phases of the cell cycle
Cyclin Dependent Kinase Regulation of Cell Cycle Genes
- Regulate cell cycle progression is by phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor gene Rb
Tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors
- Activate PI3 kinase through Ras or independently of Ras
- PIP3 interacts with the pleckstrin homology domain of Akt to recruit Akt to the plasma membrane
- Akt is then activated through phosphorylation by PDK1
- Activation results in tumor cell proliferation and survival
Akt
- Phosphorylates and inhibits a protein that allows for the activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin
- Contributes to cell cycle progression by decreasing the expression of cell cycle inhibitors
mTOR
- An evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinase that is inhibited by the drug rapamycin
- Phosphorylates the initiation factor 4EBP1
- Phosphorylates and activates p70 S6 kinase
4EBP1
- Binds to and inhibits eLF4E
- Inhibits the majority of translation
- Phosphorylation releases eLF4E allowing for initiation of translation
Cyclin dependent kinases
- Enzymes that lead the cell through the phases of the cell cycle
- Phosphorylate crucial proteins involved in cell division
- Dependent upon another group of proteins, the cyclins
- Each interacts with a different set of cyclins
Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors
- Block the actions of the cyclin-CDK pairs
- INK4 CDK inhibitors block the effects of CDK 4 and 6
- p21Waf1/Cip1, p27Kip1 and p57Kip1 act more widely to inhibit all of the cyclin-CDK complexes that form later in the cell cycle
Cyclin dependent kinases
- Regulate cell cycle progression
- As cellular levels fall, cyclin-cyclin dependent kinase complex phosphorylates Rb
E2F transcription factor
- Mediates transcription of genes responsible for cell cycle progression
- Akt phosphorylates BAD
- Bcl protein termed BAD binds to and inhibits the anti-apoptotic actions of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL
- By inhibiting BAD, Akt promotes cell survival
Apoptotic cell death includes the loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity followed by the release of cytochrome C.
Rac1
- Small G protein
- Can interact with downstream effectors PAK and LIM kinase
- A member of the Rho family of small G proteins
Lesson Oncology Treatment: VEGF Receptor Signaling in Angiogenesis is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
M.J. Cross, J. Dixelius, T. Matsumoto, L. Claesson-Welsh. VEGF-Receptor Signal Transduction. TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences. 28(9):488-494, 2003.
J.A. Forsythe et al. Activation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Transcription by Hypoxi-Inducible Factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4604-4613, 1996.
R.H. Wenger. Cellular Adaptation to Hypoxia: O2-Sensing Protein Hydroxylases, Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors, and O2-Regulated Gene Expression. FASEB J. 16:1151-1162, 2002.
C.W. Pugh, P.J. Ratcliffe. Regulation of Angiogenesis by Hypoxia: Role of the HIF System. Nat Med. 9:677-684, 2003.
O. Lliopaulos, A.P. Levy, C. Jiang, et al. Negative Regulation of Hypoxia Inducible Genes by the von Hippel Lindau Protein. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 93:10595-10599, 1996.
M. Ohh, C.W. Park, M. Ivan et al. Ubiquitination of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Requires Direct Binding to the Beta-Domain of the von Hippel-Lindau Protein. Nat Cell Biol. 2:423-427, 2000.
J.G. Herman, F. Latiff, Y. Weng, M.I. Lerman, B. Zbar, S. Liu, D. Samid, D.S. Duan, J.R. Gnarra, W.M. Linehan. Silencing of the VHL Tumor-Suppressor Gene by DNA Methylation in Renal Carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci. USA. 91:9700-9704, 1994.
K. Kondo, W.G. Kaelin, Jr. The von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Gene. Exp Cell Res. 264:117-125, 2001.
O. Hahn, W. Stadler. Sorafenib. Current Opinion in Oncology. 18:615-621, 2006.
M.J. Cross, J. Dixelius, T. Matsumoto, L. Claesson-Welsh. VEGF-Receptor Signal Transduction. TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences. 28(9):488-494, 2003.
O. Hahn, W. Stadler. Sorafenib. Current Opinion in Oncology. 18:615-621, 2006.
G. Song, G. Ouyang, S. Bao. The Activation of Akt/PKB Signaling Pathway and Cell Survival. J. Cell Mol. Med. 9(1):59-71, 2005.
A.C. Carrera. TOR Signaling in Mammals. Journal of Cell Science. 117:4615-4616, 2004.
G. Song, G. Ouyang, S. Bao. The Activation of Akt/PKB Signaling Pathway and Cell Survival. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 9(1):59-71, 2005.
M. Vicente-Manzanares, D.J. Webb, A. R. Horwitz. Cell Migration at a Glance. Journal of Cell Science. 118:4917-4919, 2005.