SMi Source lesson Biotech: Monoclonal Antibodies has the following microlearning topics
1. Antibodies and the Immune System

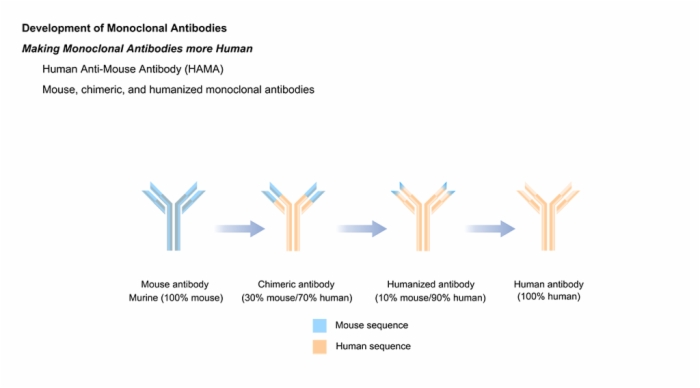
2. Development of Monoclonal Antibodies

3. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies


Lesson Biotech: Monoclonal Antibodies teaches these concepts
Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibodies and the Immune System, Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibodies and the Immune System, Antibody Structure
Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibodies and the Immune System, Antigen Binding
Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibodies and the Immune System, Antibody Production by B Cells
Monoclonal Antibodies, Antibodies and the Immune System, Antibody Function in Immune Defense
Lesson Biotech: Monoclonal Antibodies addresses these key points
Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies
- Antibodies
- The role of antibodies in the immune response
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Structure
- Production
- Improvement
- Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies
- Mechanisms of action
- Oncology
- Autoimmune diseases
- Other diseases
- Emerging trends
Antibody structure
- Antibody; a protein produced by the immune system to recognize foreign molecules on pathogens
- Antigen; a foreign molecule recognized by, and bound by, an antibody
- Immunoglobulin (Ig); a class of protein representing all antibodies
- Immunoglobulin types; the A, D, E, G and M sub-types of immunoglobulin, each with a specialized role in immune defense. IgG is most often used for biotech/medical applications
Antigen Binding
- Epitope: the region of an antigen molecule responsible for eliciting antibody production and antibody binding
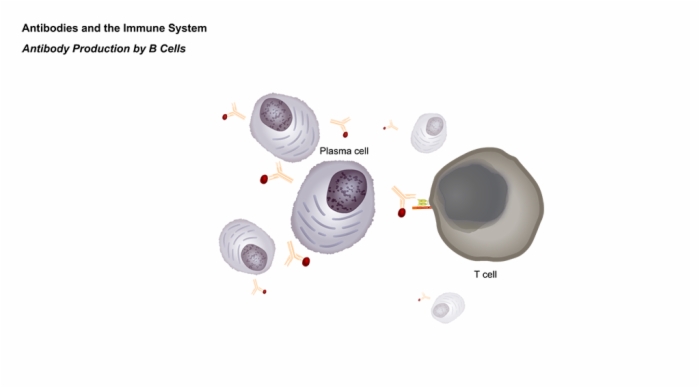
Antibody Production by B Cells
- Antibodies are produced by B cells, a specialized type of lymphocyte, as a key part of the adaptive immune response
- In addition to antibody-producing plasma cells, T cell engagement also stimulates the formation of memory B cells, which retain a memory of how to produce a particular monoclonal antibody for very long periods.
Antibody Function in Immune Defense
- Antibodies combat foreign pathogens in different ways
- IgG molecules will coat a pathogen, presenting a complex that can be recognized by white blood cells such as macrophages and neutrophils
- Alternatively, antibody-antigen complexes can recruit the complement system which destroys foreign bacteria and parasites in different ways
Lesson Biotech: Monoclonal Antibodies is built from these main references. Log into SMi Source for a complete list and details.
Janeway, CA Jr, Travers, P, Walport, M, Shlomchik, MJ. Immunobiology. The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. Chapter 2. Garland Science (2001)
Janeway, CA Jr, Travers, P, Walport, M, Shlomchik, MJ. Immunobiology. The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. Chapter 3. Garland Science (2001)
Lesson Biotech: Monoclonal Antibodies introduces and defines these terms
Epitope: The region of an antigen molecule responsible for eliciting antibody production and antibody binding.