SMi Source lesson Cardiovascular: Clot formation and Vascular Injury has the following microlearning topics
1. Blood Clot Formation

Lesson Cardiovascular: Clot formation and Vascular Injury teaches these concepts
Vascular Injury, Effects, Blood Clot Formation
Lesson Cardiovascular: Clot formation and Vascular Injury addresses these key points
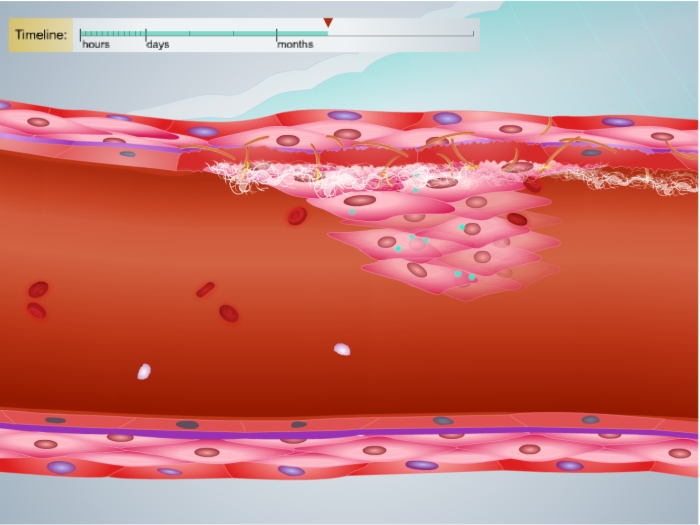
- Vascular surgery creates vascular injury at the anastomosis.
- Upon vascular injury:
- The endothelial cell lining of the vessel lumen is disrupted and the underlying smooth muscle and collagen fibers are exposed to the circulation.
- Von Willebrand Factor binds to exposed collagen fibers through its A3 domain.
- Collagen-bound von Willebrand Factor then binds to platelets through the GP Ibα receptor.
- This interaction acts to tether platelets to thrombogenic surfaces even during rapid blood flow.
- Shear forces from blood flow propel the tethered platelet forward where it comes in contact with exposed collagen.
- The platelet then binds collagen through integrin receptors, and platelet activation occurs.
- Activated platelets release a variety of factors that attract and activate additional platelets at the site of injury to amplify platelet aggregation.
- Additional clotting mechanisms result in the production of fibrin which forms dense interlocking strands which help to secure the clot.
- Over time, the factors released by activated platelets also attract vascular smooth muscle cells from the media and adventitia to migrate to the intima of the vessel wall.
- As these smooth muscle cells migrate and proliferate they cause thickening of the vessel wall and narrowing of the lumen.
- This narrowing restricts blood flow and may eventually lead to thrombosis and complete occlusion of the blood vessel.