SMi Source lesson Diabetes: Anatomy and Physiology has the following microlearning topics
1. Introduction: Anatomy and Physiology of Diabetes


2. Organs Involved in Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetes


3. Intracellular Glucose Processing

4. GLUT transporters

5. Knowledge Check: Glucagon Signaling Definitions


6. Knowledge Check: Glucagon and Insulin Signaling


7. Glucose Homeostasis

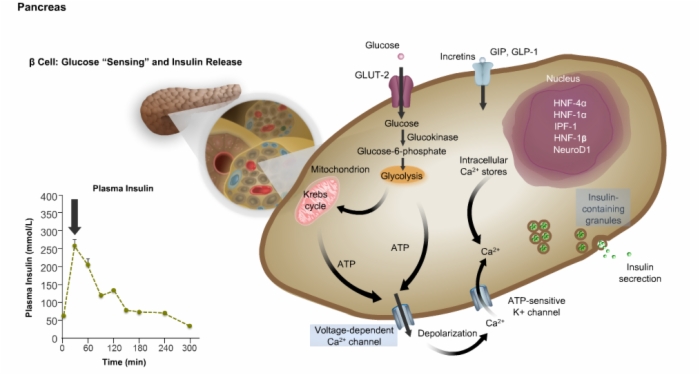
8. Beta Cell: Glucose Sensing and Insulin Release

9. Biphasic Insulin Secretion
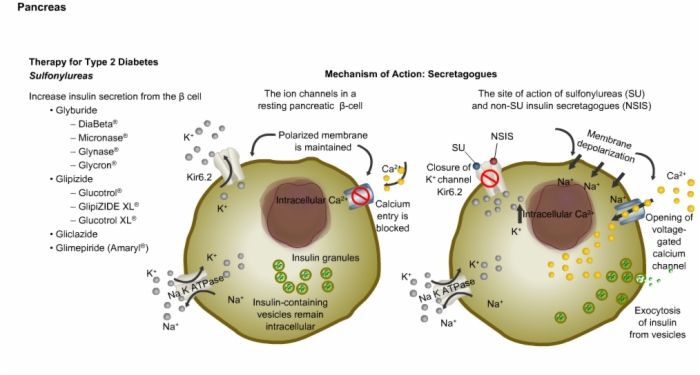

10. Pancreatic Beta Cells, Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
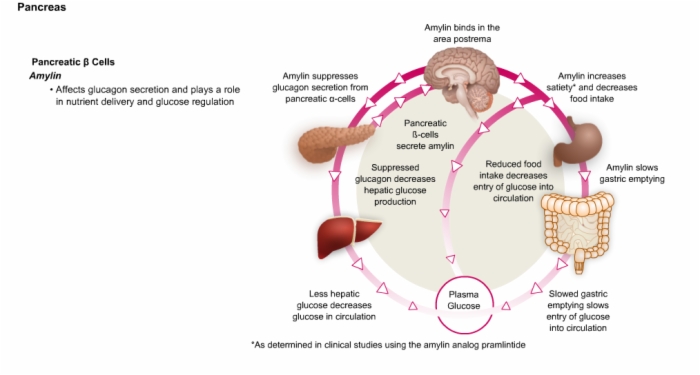

11. Pancreatic Alpha and Delta Cells, Pancreatic Function in Diabetes


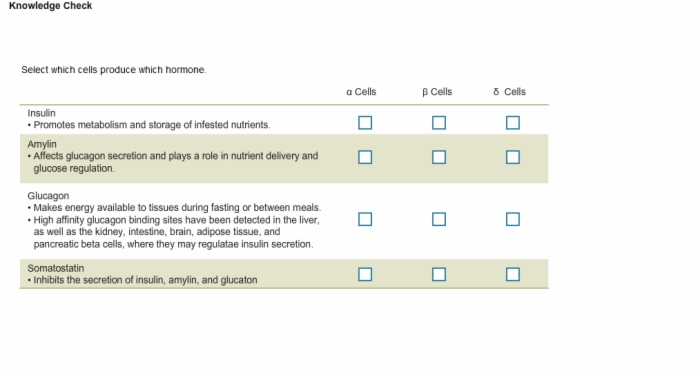
12. Knowledge Check: Hormone Production

13. Knowledge Check: Counter-Regulatory Hormones


14. Knowledge Check: Biphasic Insulin


15. Adipose Tissue: A New Endocrine Organ
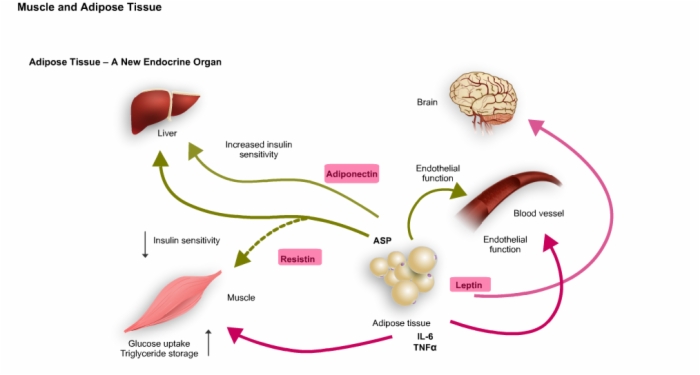

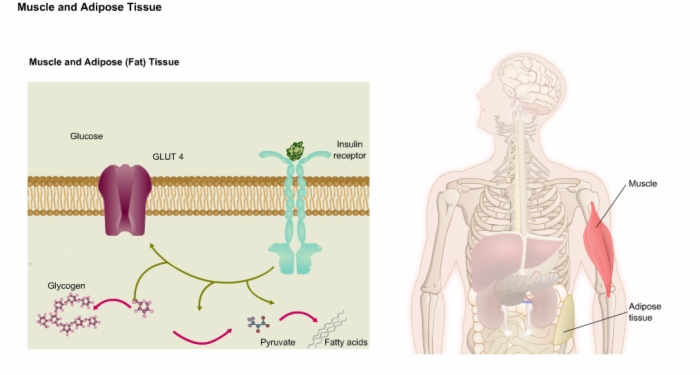
16. Muscle and Adipose (Fat) Tissue

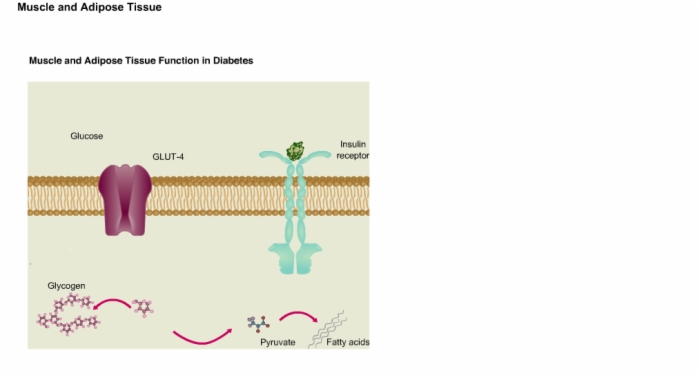
17. Muscle and Adipose Tissue Function in Diabetes

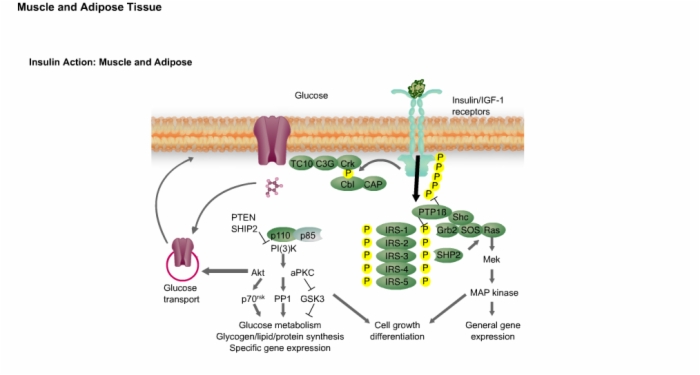
18. Insulin Action: Muscle and Adipose

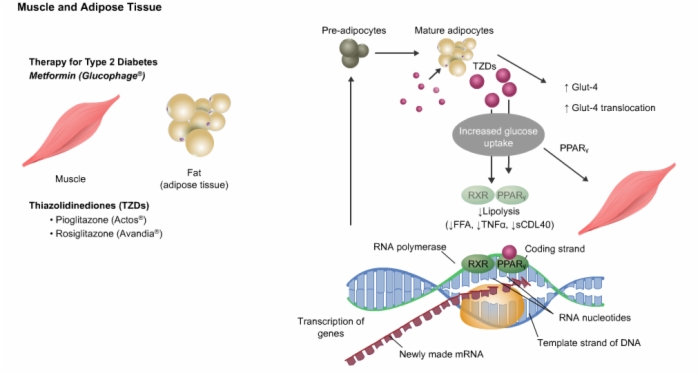
19. Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes

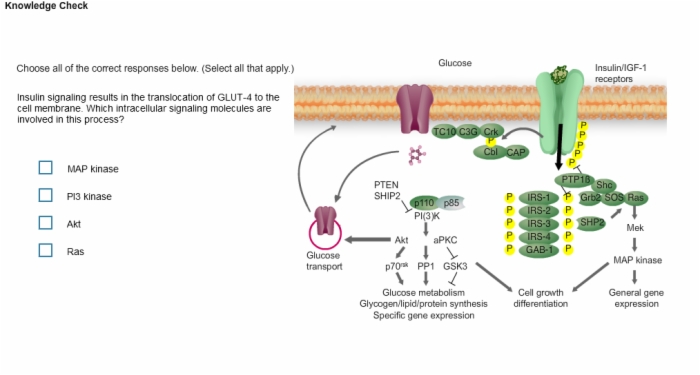
20. Knowledge Check: Insulin Signaling

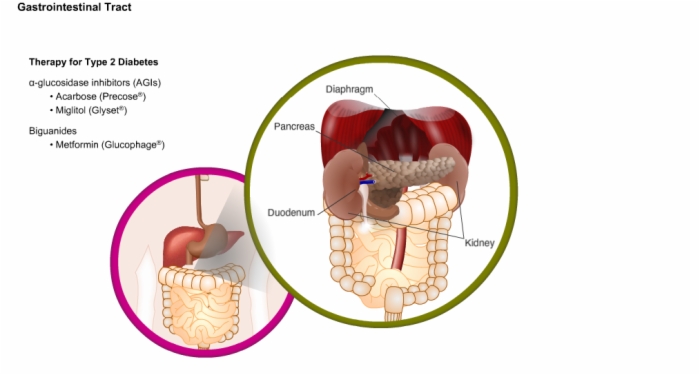
21. Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes, Stomach

22. Intestinal L Cells, Other Intestinal Endocrine Cells


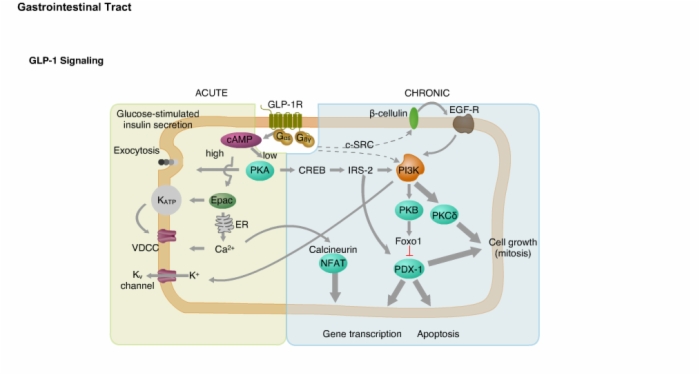
23. GLP-1 Signaling and DPP-4

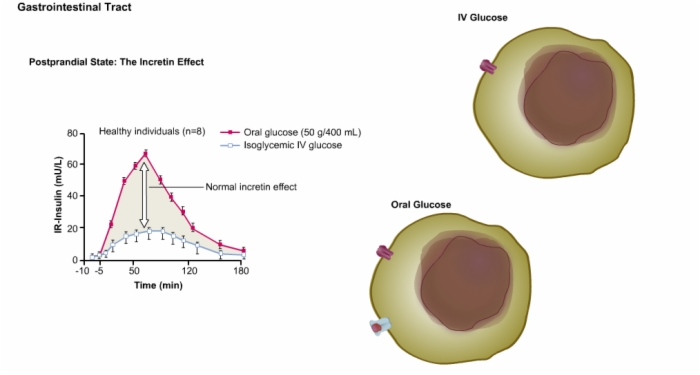
24. Postprandial State: The Incretin Effect

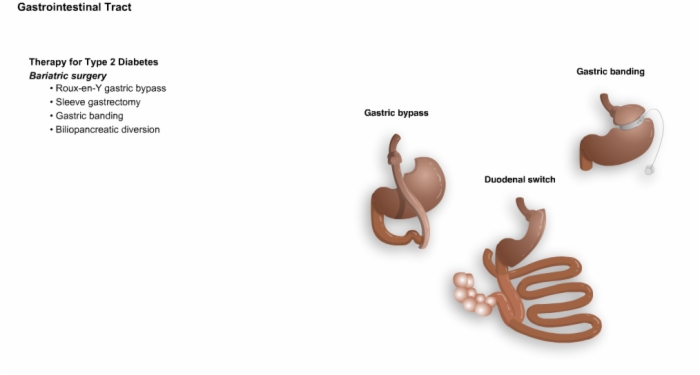
25. Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes, Bariatric Surgery

26. Knowledge Check: The Incretin Effect


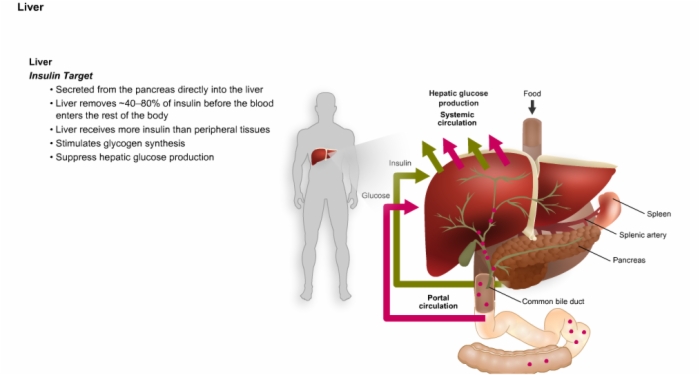
27. Liver Function

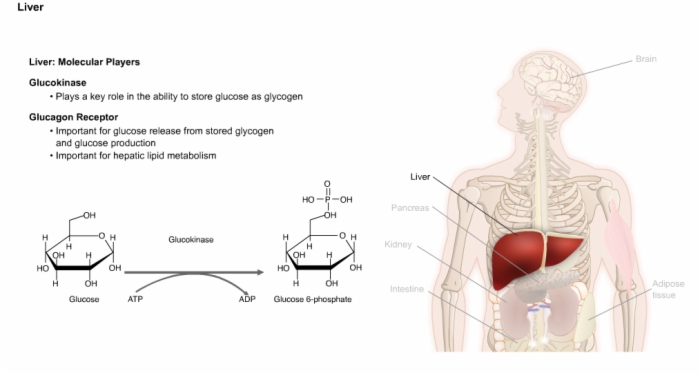
28. Liver: Molecular Players

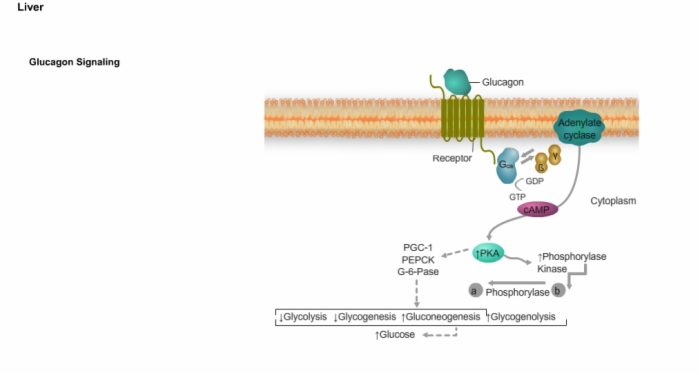
29. Glucagon Signaling

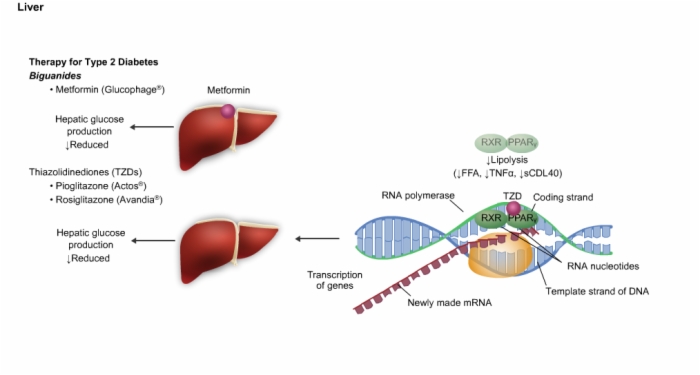
30. Liver Function in Diabetes, Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes

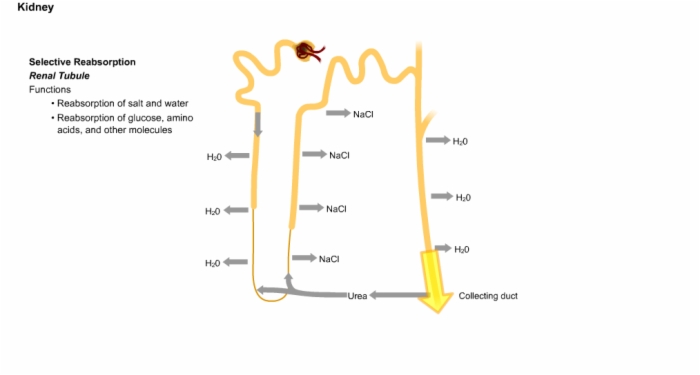
31. Kidney Function

32. Kidneys

33. Kidney Function in Diabetes

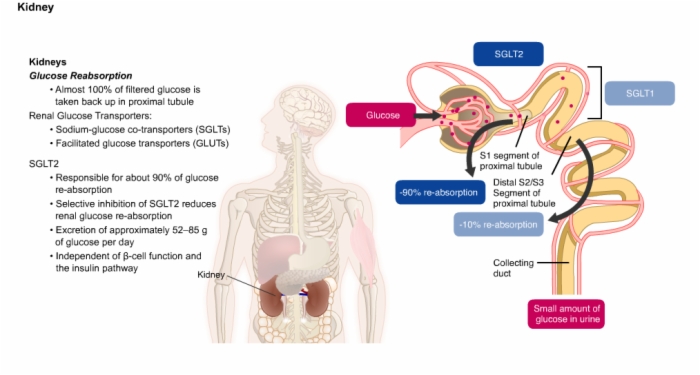
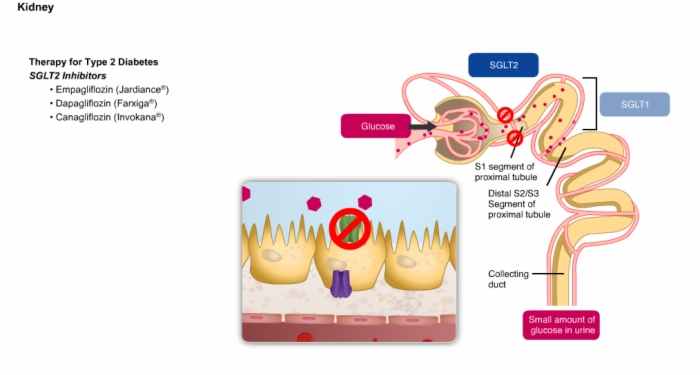
34. Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes: SGLT2 Inhibitors

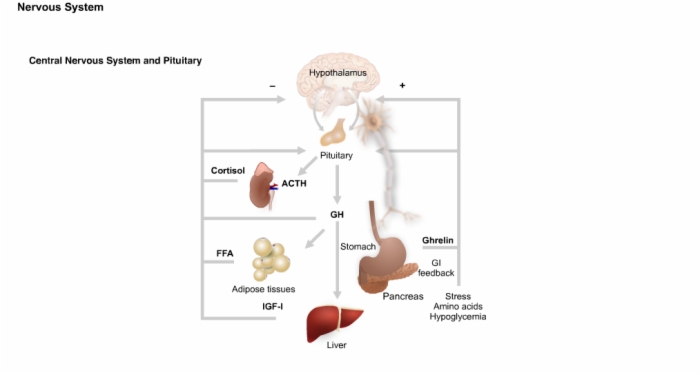
35. Central Nervous System and Pituitary

36. Diabetes: Anatomy and Physiology: Summary


Lesson Diabetes: Anatomy and Physiology teaches these concepts
Anatomy and Physiology of Diabetes, Introduction: Anatomy and Physiology of Diabetes
Lesson Diabetes: Anatomy and Physiology addresses these key points
Insulin is necessary for the body to be able to use glucose for energy
Organs involved in diabetes include
- Pancreas
- Brain
- Liver
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Muscle
- Kidney
- Other systems
Organs and hormones act in concert to maintain appropriate glucose levels
Diabetes is a disease characterized by a deficit in glucose homeostasis
Glucose homeostasis plays a crucial role in survival